Moon Near the Beehive Cluster — March 26
1. What this event is On March 26, the Moon appears very close in the sky to the Beehive Cluster, a famous open star cluster. This is called a close conjunction in astronomy. It doesn’t mean the Moon is physically near the cluster in space they only appear close from our viewpoint on Earth. 2….
New Observations of Gas Clouds Offer Insight Into Supermassive Black Hole Dynamics
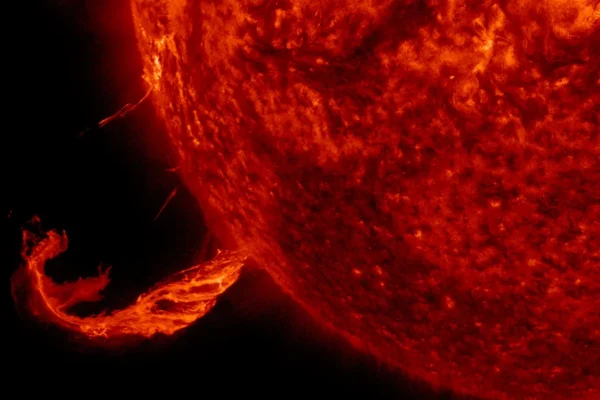
Astronomers studying the center of our galaxy have uncovered a fascinating cosmic mystery: several strange gas clouds moving in tight orbits around the supermassive black hole at the heart of the Milky Way. These clouds are providing scientists with new clues about the extreme environment surrounding the galaxy’s central black hole, known as Sagittarius A*….
Cosmic Wonders: Incredible Space Discoveries Changing Our Understanding of the Universe
In recent years, astronomers have been uncovering extraordinary discoveries that are transforming our understanding of the universe. Thanks to powerful telescopes, advanced space missions, and improved data analysis, scientists are revealing cosmic phenomena that once seemed impossible. From wandering planets drifting through deep space to mysterious signals from distant stars, these findings highlight just how…
Lunar “X” and “V” Effect — March 25
The Lunar X and V Effect is a fascinating optical phenomenon that appears on the surface of the Moon for a short time each month. It occurs when sunlight strikes certain lunar craters at a very specific angle near the terminator the line dividing the illuminated and dark sides of the Moon. Because of this…
Moon Close to the Pleiades — March 23
The event Moon close to the Pleiades on March 23 is a beautiful astronomical conjunction where the Moon appears very near the Pleiades in the night sky. The Pleiades is a famous open star cluster located in the constellation Taurus. During this event, the Moon passes close to the cluster from our perspective on Earth…
Scientists Explain How the Night Sky Lets Us See Billions of Years Into the Past
Every time humans look up at the night sky, they are not just observing distant stars , they are witnessing moments from the past. Scientists often describe astronomy as a form of cosmic time travel, because light from distant objects takes time to reach Earth. As a result, telescopes and even the human eye reveal…
Scientists Capture Rhythmic Heartbeat Signals From a Star Thousands of Light-Years Away
Astronomers have detected unusual rhythmic signals—described as a cosmic “heartbeat”—coming from a distant star system, offering new insights into how stars interact in extreme environments. The discovery has sparked excitement among scientists, who say the phenomenon could help them better understand stellar evolution and gravitational interactions in binary star systems. The signals were identified by…
Gamma Normid Meteor Shower — Peak around March 14–15
The Gamma-Normid Meteor Shower — A Quiet Cosmic Display The Gamma‑Normid Meteor Shower is one of the lesser known meteor showers of the year yet it offers a beautiful glimpse of cosmic activity in the night sky. Unlike famous meteor showers that produce dozens of meteors every hour, this one is more subtle and peaceful…
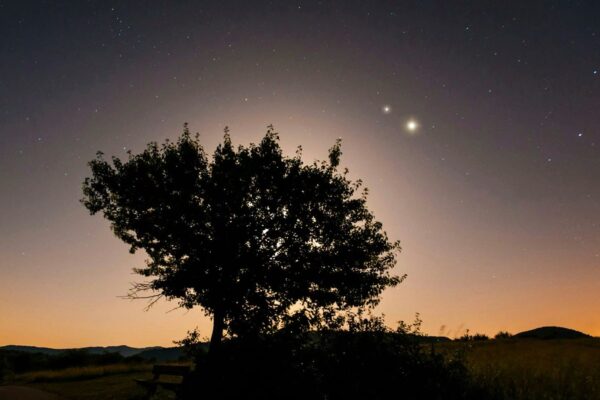
Mercury–Mars Conjunction — March 14, 2026
A Rare Planetary Meeting in the Evening Sky On March 14, 2026, the inner planet Mercury and the red world Mars will appear unusually close together in the sky in an event known as a planetary conjunction. During this celestial alignment, the two planets will seem to nearly touch from our viewpoint on Earth even…
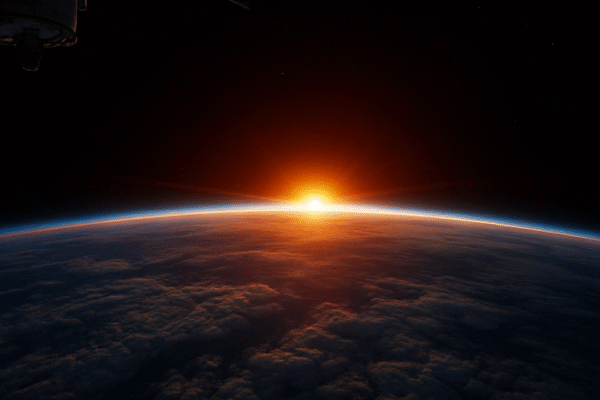
March Equinox 2026: Sun, Earth, and the Celestial Balance Explained
Chattogram, Bangladesh – March 8, 2026: Every year, the Earth experiences a moment of cosmic equilibrium known as the March Equinox, a celestial event that signals a pivotal transition in the planet’s seasons. This year, astronomers confirm that the equinox will occur on March 20, 2026, when day and night are nearly equal in length…