The Earth-Moon-Sun System: Geometry of Seasons & Eclipses
The Earth–Moon–Sun System
A perfectly balanced cosmic dance controlled by gravity and motion.

The Earth–Moon–Sun system is a gravitational system where three celestial bodies move in a perfectly balanced pattern. The Earth revolves around the Sun once every 365.25 days and rotates on its axis every 24 hours, creating day and night. The Moon revolves around the Earth every 27.3 days and rotates in the same time, which is why only one side of the Moon is visible from Earth. The Earth’s axis is tilted at 23.5° and the Moon’s orbit is tilted by 5° and these two tilts are the main reasons behind seasons and eclipses.
The Real Cause of Seasons
Seasons are created by Earth’s tilt not by its distance from the Sun
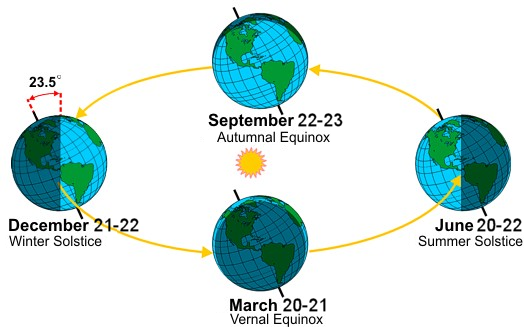
Seasons are caused by the tilt of Earth’s axis not by the distance between the Earth and the Sun. As Earth moves around the Sun different hemispheres receive different angles of sunlight. When the Northern Hemisphere tilts toward the Sun, it receives direct sunlight and experiences summer while the Southern Hemisphere experiences winter. When the Northern Hemisphere tilts away from the Sun, winter occurs there and summer occurs in the Southern Hemisphere. The changing angle of sunlight controls temperature, climate and day length.
3. Equinoxes and Solstices
These four key positions divide the year into seasons.
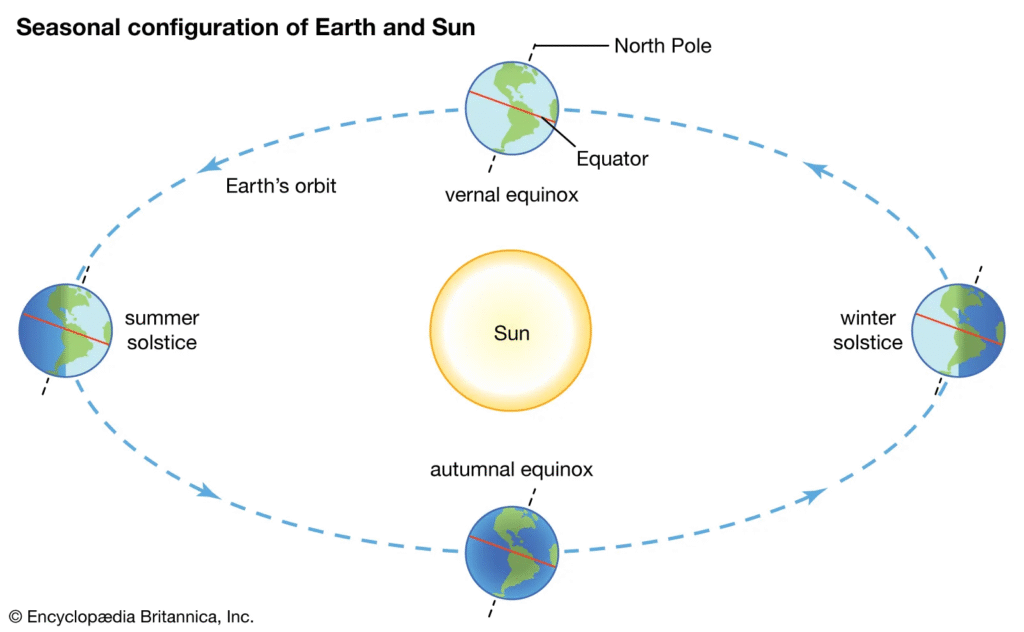
The Earth experiences four major seasonal positions during its revolution around the Sun. The March and September equinoxes are the times when day and night are almost equal everywhere on Earth. The June solstice marks the longest day in the Northern Hemisphere while the December solstice marks the shortest day. These positions are responsible for the regular seasonal cycle observed every year.
Phases of the Moon
Moon phases are shaped by sunlight and changing angles.
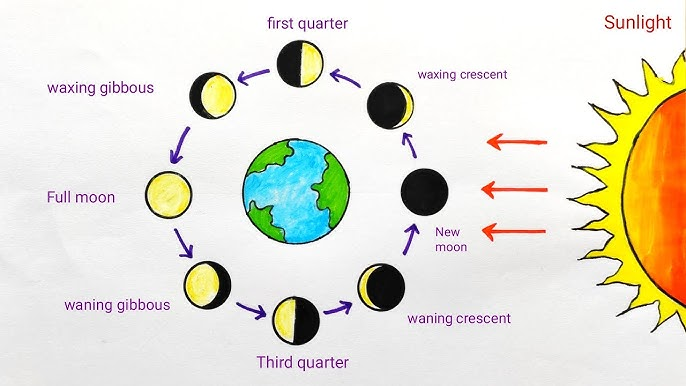
The Moon goes through different phases such as new moon, crescent, quarter, gibbous and full moon. These phases occur because different portions of the Moon are illuminated by the Sun as the Moon orbits the Earth. The phases are not caused by Earth’s shadow; they are simply the result of changing viewing angles between the Sun, Earth and Moon.
What Is a Solar Eclipse
The Moon temporarily hides the Sun from Earth.
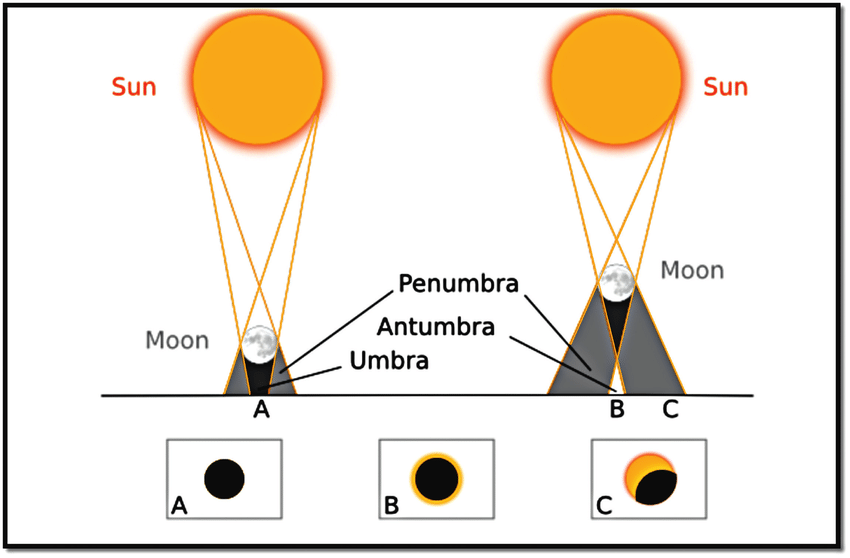
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon comes between the Sun and the Earth and blocks sunlight partially or completely. A total solar eclipse happens when the Sun is fully covered by the Moon, a partial solar eclipse occurs when it is only partly covered, and an annular eclipse occurs when a bright ring of the Sun remains visible. During a total solar eclipse, scientists can observe the Sun’s outer atmosphere called the corona.
What Is a Lunar Eclipse
Earth’s shadow slowly darkens the Moon.
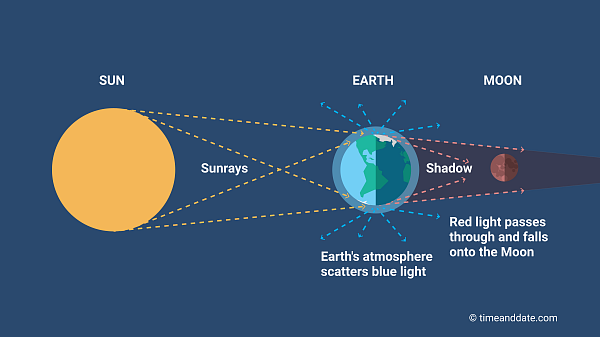
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon causing Earth’s shadow to fall on the Moon. Lunar eclipses can be total, partial or penumbral. During a total lunar eclipse, the Moon appears red due to the bending and scattering of sunlight through Earth’s atmosphere which is why it is often called a “blood moon.”
Why Eclipses Do Not Happen Every Month
A small orbital tilt prevents frequent eclipses.
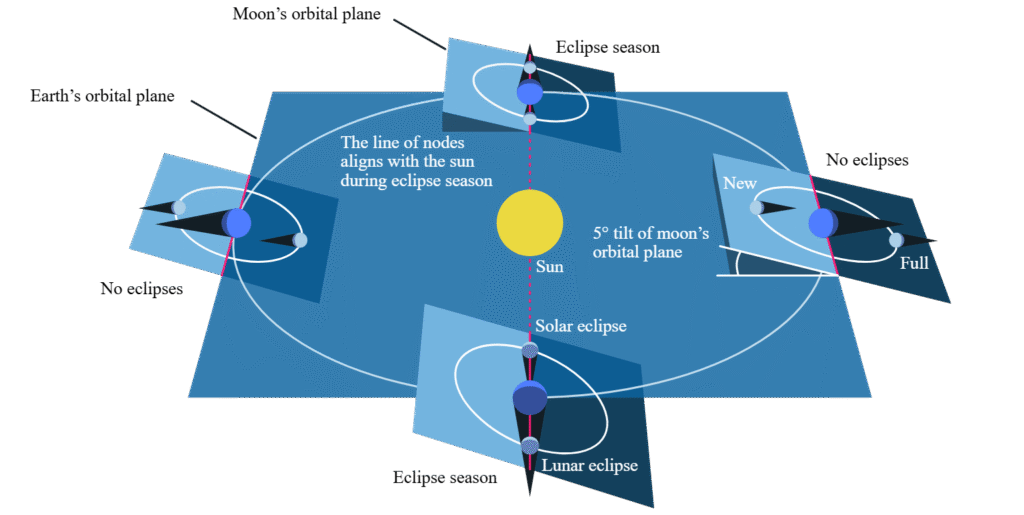
Eclipses do not occur every month because the Moon’s orbit is tilted by about 5° relative to Earth’s orbit around the Sun. Most of the time, the Moon passes above or below Earth’s shadow. Eclipses only occur during special periods called eclipse seasons, which happen about twice each year.
Seasons vs Eclipses
Seasons last for months, eclipses last for moments.
Seasons are long term changes caused by Earth’s tilt and last for months while eclipses are short term events caused by perfect alignment and last for only a short time. Seasons affect climate, agriculture and daily life whereas eclipses are rare astronomical events used for scientific research and also hold cultural significance.
Final Summary
Tilt creates seasons, alignment creates eclipses.
The geometry of the Earth–Moon–Sun system controls two of the most important natural phenomena observed from Earth seasons and eclipses. Earth’s tilted axis causes the seasons, while the perfect alignment of the Sun, Earth, and Moon creates solar and lunar eclipses.


9552betcom is another betting site I’ve used. Nothing super special, but it gets the job done. Decent selection of sports and markets. Have a look and see if it fits your needs 9552betcom.
Terms are heard tho🤧
Alright, let’s talk xo888vip. Feels a bit fancier than the others. I liked the VIP treatment and they seem to be more focused for pros like me! Check this site out! –> xo888vip
Heard some chatter about Adda52 ban. What’s the story? Is it true? Anyone know the official stance? Check them anyway, if it’s still up: adda52ban
Looking for the 188bet download? cachvao188bet.net got me covered. Quick and easy download, no messing around. Download it here: 188bet download
Visit Site – Layout is crisp, browsing is easy, and content feels trustworthy and clear.
Xosokh, huh? Sounds kinda cool. Anyone else tried it out? Hoping it’s legit and not some kinda scam. Might test my luck and see where it takes me at xosokh
professional networking site – Easily browse useful links and resources without any hassle.
discover new angles – Browsing here made it easy to think differently about next steps.
look around – Easygoing style, it makes discovery feel natural.
SavvyShopperHub – Emphasizes smart spending and great value options.
click here – Organized sections, responsive pages, first impression is positive
xavix access – Professional feel, easy-to-use interface, and smooth site experience
focusbuildsenergy network – Clear sections, straightforward layout, and pages are quick to load
Zavro Express – Browsing seamless, pages responsive and checkout steps simple.
ravixo info – Smooth browsing, helpful text, and fast page load times
DigitalCartPro – Easy-to-navigate, online buying is straightforward and quick.
Nhiều người vẫn hiểu lầm rằng tất cả các trang nhà cái đổi thưởng đều là cờ bạc trá hình và bất hợp pháp. Thực tế, download 888slot hoạt động dưới sự giám sát của các tổ chức cấp phép uy tín trong ngành iGaming quốc tế. Nền tảng này tuân thủ nghiêm ngặt các quy định về chống rửa tiền, bảo vệ người chơi và chơi game có trách nhiệm. TONY01-14
cavix source – Informative site that keeps things clear and uncluttered
check xelio – Layout is clear, navigation is smooth, and information is presented well
Open capital homepage – Early impression is positive, seems worth reviewing in more detail.
qerly site – Neatly structured pages, simple navigation, and content flows naturally
velon info – Clean and organized layout, content is readable and easy to follow
vexla info – Pages load quickly, interface is smooth, and content is easy to digest
TrustedCartHub – Reliable and well-structured, checkout is fast and worry-free.
velixo hub – Clear interface, tidy sections, and information is easy to find quickly
Check capital details – Organization is logical, making it simple to find relevant topics quickly.
Official trust site – Layout is simple and easy to follow, making it handy for quick learning online.
loryx info – Neat design, interesting content, and navigation keeps you moving forward
Learn more here – The site feels solid, with content that’s easy to scan and understand.
Project overview – An interesting idea overall, and the content feels direct and user-friendly.
Primary platform – The overall experience feels polished and easy to browse.
UlvorDirect – Pages open instantly, design clean, and navigation intuitive.
ideas journey – Messaging highlights movement and practical execution of concepts.
strongholdadvisors.bond – Tidy layout, site feels organized and information is easy to follow.
Primary trust link – The site feels reliable, and pages transition quickly without lag.
clarity page – Content flows naturally and highlights the main concepts clearly.
zylavoline details – Quick loading supports easy reading and clear communication.
Line overview page – Easy-to-navigate structure helps visitors understand the key points quickly.
clarity access – Messaging emphasizes rapid progress while maintaining thoughtful clarity.
discover your options – Language motivates reflection and forward movement in an engaging way.
shop savings hub – Smooth platform, browsing for deals is intuitive and quick.
bond clarity portal – Clear security info helps users feel confident while exploring bonds.
Growth-focused website – A useful-looking platform that’s easy to explore.
discover your focus – Text makes the concept of focus feel approachable and useful.
alliances insight center – Useful resources, helps build strong professional and commercial connections.
Corporate relationship network – Clean design with content that’s easy to understand.
clicktolearnandgrow.click – Found this today, content seems helpful and worth checking again.
clarity guide – Messaging is focused and encourages progress with intent.
Idea discovery platform – The structure is user-friendly and easy to follow.
Strategic business partnerships – Smart concept, the explanations feel practical and relevant.
networkingecosystemhub – Found the platform intuitive and practical, perfect for expanding business networks.
Corporate alliance network – Professional look, the concept aligns well with business growth goals.
futurestoreonline – Sleek platform, really simplifies modern shopping routines.
dealzone – Excellent resource, items were easy to locate.
careeradvancementresources – Excellent guidance for professional learning, really helped improve abilities efficiently.
pathwaynavigator – Guidance that provided clarity on complex career choices.
H5 creative platform – Clean and appealing, encourages trying out more sections.
dealgrabberonline – Couldn’t believe the discounts, great variety as well.
smartbuydigital – Premium items and secure payment system make shopping easy.
animated browsing site – Random click led here, site feels fast and easy to move through.
EV Liberty official hub – Honest content, simple layout, and very responsive pages.
child development site – Reading this felt reassuring, with a strong balance of care and expertise.
Manisa sightseeing guide – The layout is simple and the information feels reliable and practical.
enterpriseorganizationclick – Clear framework suggestions, really enhanced team efficiency today.
RI Tech news online – Layout is simple and information is easy to scan and understand.
capital resource portal – Clear presentation and simple navigation make capital info easy to grasp.
nevironexus resource – Nicely arranged content with a smooth overall flow.
holdings resource site – Clean design with holdings info that is easy to follow and professional.
TaskPilot – Tools provide accurate monitoring for easier workflow.
QunixPoint – Easy access to features, interface makes everything straightforward to understand.
zylavo capital official – Information loads rapidly, and the modern layout improves reading comfort.
TrixoHelpDesk – Every inquiry I had was handled swiftly and clearly.
NolaroControl – Allows for efficient organization and effortless tracking.
this platform – Landed here randomly and found the structure surprisingly user-friendly.
check this out – Navigation is smooth, and content is presented in a clear and understandable way.
crystalcorner2.shop – The most stunning gems and crystals, absolutely love browsing this site.
curtaincraft.shop – Great variety of textiles, easy to find the perfect curtains for your space.
freshfinder.shop – A fantastic site with unique finds, always something exciting to discover!
this platform – Information is neatly arranged and the site feels reliable.
check zarvo – Fast loading pages, intuitive navigation, and content is easy to follow.
Briovista Essentials – The design is so classy, and the product range is simply impressive.
ulixo portal link – Checked it out today, layout is clear and browsing is fast.
craftcabin.shop – An amazing spot for crafters, always full of fresh and creative materials!
dorvani.shop – Wonderful selection of trendy and useful products, great for all my needs!
open zorivohold – First glance showed clear organization and a polished look.
charmcartel.shop – Great selection of trendy accessories, very smooth shopping experience.
halvessa.shop – A sleek and minimalistic design, perfect for finding unique items.
irevana online shop – Decent variety, site runs clean and feels dependable.
elvarose.shop – Always find something beautiful here for my home!
Quenvia Hub – Attractive design, moving through categories was fast and stress-free.
Orla Deals – Fantastic variety of items, buying felt fast and easy.
Discover Marqvella – Really enjoying the aesthetic here, everything feels clean, intentional, and current.
Pantry Basics Shop – Simple layout, finding products takes no effort.
Ruvina Select – Simple layout, images are detailed and shopping experience felt smooth.
Oracle Discounts – Tons of savings, browsing is simple and efficient.