Unveiling the Universe’s Deepest Mystery: The Star That Hides a Black Hole

Imagine a star so vast, it hides a secret within! Astronomers have made an astonishing discovery: black holes nestled inside giant stars, revealing a new class of celestial objects.
The universe never ceases to amaze us! In a groundbreaking revelation, astronomers have announced the astonishing discovery of black holes hidden inside giant stars. This incredible finding—made possible through advanced data analysis—opens up a whole new frontier in our quest to unravel the universe’s most profound mysteries.
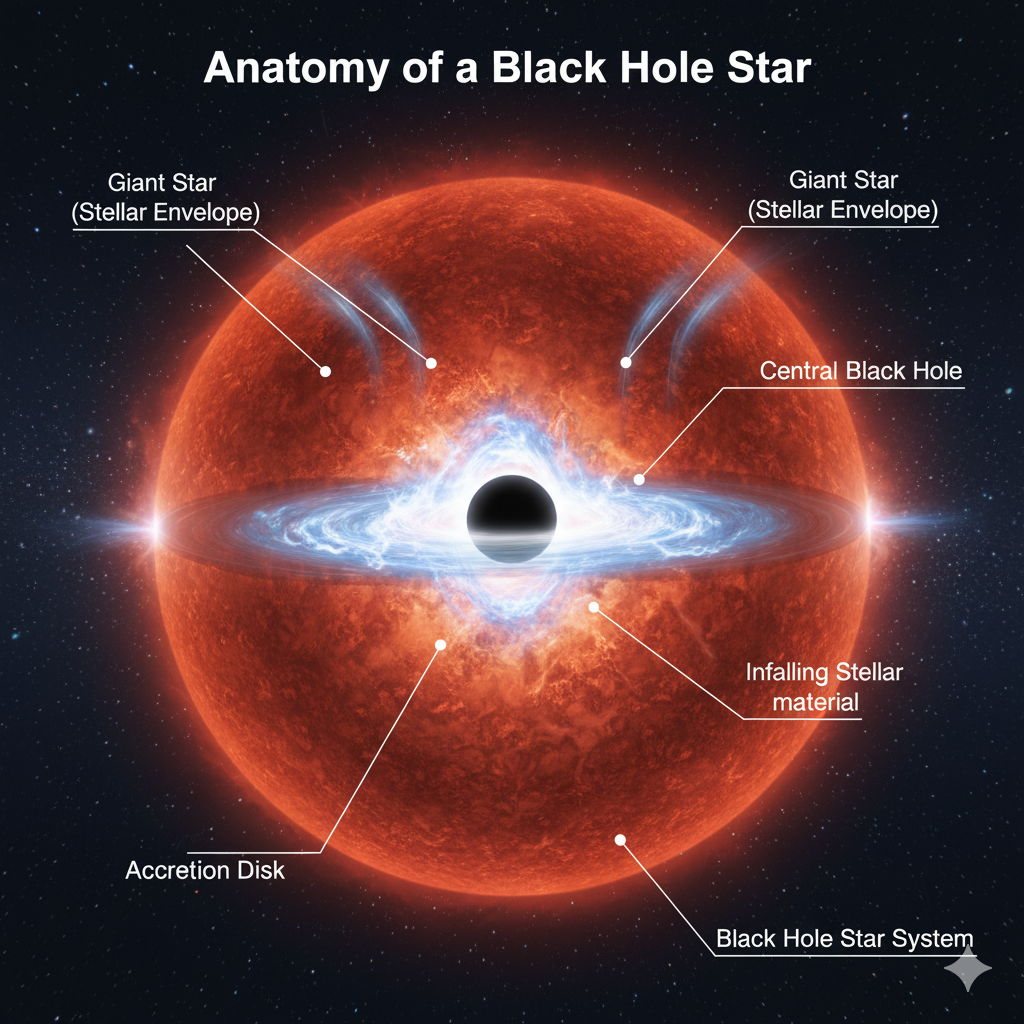
The Black Hole Star Phenomenon
According to researchers, certain massive stars may actually form and evolve around a central black hole. Over billions of years, these stars grow so immense that they completely envelop the black hole within their stellar material. This isn’t a destructive event, however. Instead, the star’s matter fuels the central singularity, allowing the black hole to grow even more powerful as it quietly consumes its host from the inside.
Scientists are calling this phenomenon a kind of “Cosmic Nesting Doll”—a celestial matryoshka where one enigmatic world is concealed within another.
This discovery is helping to resolve several puzzling astronomical observations:
- It explains why some large stars exhibit unusually erratic behavior.
- It offers a new mechanism for why certain black holes appear to grow at an unexpectedly rapid rate.
Researchers anticipate that this finding will necessitate a revision of current stellar evolution models and offer unprecedented insights into the life cycles of stars and the formation of black holes. They have tentatively dubbed these new celestial bodies a distinct category: “Black Hole Stars.”
Understanding Black Holes
To appreciate the significance of this discovery, it helps to review the nature of black holes:
| Component | Description |
| Definition | A region in spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape. |
| Formation | Typically occurs when a very massive star collapses under its own weight after a supernova explosion. |
| Singularity | The infinitesimally small, infinitely dense point at the center of the black hole where matter is crushed. |
| Event Horizon | The boundary surrounding the black hole; crossing this point means nothing can ever return. |
The Data Behind the Breakthrough
This groundbreaking research was conducted by multiple teams of scientists across the United States and Europe. Their primary methodology involved analyzing extensive data, particularly from the cutting-edge James Webb Space Telescope (JWST).
JWST’s superior sensitivity and deep infrared observational capabilities allowed the teams to detect subtle spectral signatures and unusual luminosity characteristics within giant stars that strongly suggested the presence of hidden, dense objects—the black holes. The analysis of these complex data sets provided the first concrete evidence that some massive stars are, indeed, harboring black holes within their cores.
The Implications for Astrophysics
The existence of Black Hole Stars has profound implications for our understanding of the cosmos:
- Challenging Stellar Models: Existing theoretical models of massive star lifecycles must now be revised to account for stars that incorporate black holes, especially concerning energy balance and stability.
- Black Hole Growth: This discovery offers a crucial, new pathway for the growth of black holes, potentially solving the long-standing mystery of how some intermediate-mass black holes accumulate mass so quickly.
- New Observational Targets: Astronomers now have a completely new class of objects to target. Future surveys will focus on identifying specific stellar behaviors that might indicate a hidden black hole, guiding new missions and observations.
The universe continues to reveal its secrets in the most unexpected ways. The “Black Hole Star” is a testament to the fact that even within the known mechanics of space, there are still layers upon layers of mystery waiting to be uncovered, pushing the boundaries of physics and astronomy.
What are your thoughts on this incredible new paradigm in stellar evolution?


Basic strategy’s all about minimizing losses, right? Seeing platforms like nustar game apk offer easy deposits (GCash is a plus!) makes getting in the game simpler. Verification is key for smooth withdrawals, though! 😉
Great breakdown! As a designer, Lovart’s AI-driven canvas and multi-tool integration could really streamline workflows-Lovart is shaping up to be a game-changer for creative pros.
That’s a fascinating take on baccarat strategy! Thinking about manipulating visuals with simple language – like with AI Nano Banana– feels similarly intuitive. Simplifying complex tasks is key, right? Great post!
Yo, just tried out thabet777vn! Pretty good experience, especially if you’re into this kind of stuff. The graphics are decent and the gameplay is smooth. Worth giving a shot! You can try it here: thabet777vn.
Interesting article! Seeing more platforms like phil168 casino cater specifically to the Philippine market is smart. KYC verification is key for trust, and localized payment options like GCash are a huge plus for players!
Interesting analysis! Seeing more platforms like wowph vip cater to the Filipino market is great. Quick registration & payouts are key – under 30 seconds is impressive! Hoping for responsible gaming too.
Interesting read! Managing risk is key, not just in poker, but with any online entertainment. Seeing platforms like arion play link prioritize safety & responsible gaming is a good sign for PH players. Solid compliance is crucial!
X1111game? Sounds kinda mysterious but let’s see what’s poppin’. Hoping it’s not another scam site. Anyone got the inside scoop before I drop some cash? x1111game
E aí, nerds! A 9dgame7 tem uns jogos super diferentes e inovadores. Tô curtindo explorar as opções e testar minhas habilidades. Pra quem gosta de jogos fora da caixa, vale a pena conferir!
Having trouble finding the right login? 813betlogin makes it super simple to get back into the action. Fast, secure, and easy to use. No more password headaches! 813betlogin
Ok3655vn? Not bad, not bad at all. I love the variety of gaming options and it’s not hard to navigate. Check it out –> ok3655vn
Maxwinexchlogin – the login process was straightforward, at least! Can’t say too much beyond that without getting in. Easy peasy lemon squeezy access at maxwinexchlogin!